Cathode Ray Tube (CRT):
CRT stands for Cathode Ray Tube. CRT is a technology used in traditional computer monitors and televisions. The image on CRT display is created by firing electrons from the back of the tube of phosphorus located towards the front of the screen.
Once the electron heats the phosphorus, they light up, and they are projected on a screen. The color you view on the screen is produced by a blend of red, blue and green light.
Components of CRT:
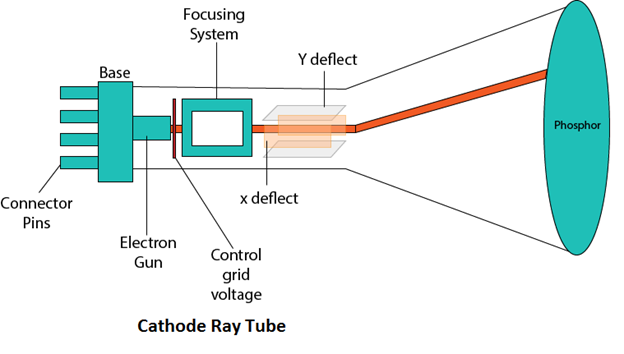
Main Components of CRT are:
1. Electron Gun: Electron gun consisting of a series of elements, primarily a heating filament (heater) and a cathode. The electron gun creates a source of electrons which are focused into a narrow beam directed at the face of the CRT.Control Electrode: It is used to turn the electron beam on and off.
3. Focusing system: It is used to create a clear picture by focusing the electrons into a narrow beam.
4. Deflection Yoke: It is used to control the direction of the electron beam. It creates an electric or magnetic field which will bend the electron beam as it passes through the area. In a conventional CRT, the yoke is linked to a sweep or scan generator. The deflection yoke which is connected to the sweep generator creates a fluctuating electric or magnetic potential.
5. Phosphorus-coated screen: The inside front surface of every CRT is coated with phosphors. Phosphors glow when a high-energy electron beam hits them. Phosphorescence is the term used to characterize the light given off by a phosphor after it has been exposed to an electron beam.
Cathode Ray Tubes (CRT) –
A cathode ray tube (CRT) is a specialized vacuum tube in which images are produced when an electron beam strikes a phosphorescent surface. It modulates, accelerates, and deflects electron beam(s) onto the screen to create the images. Most desktop computer displays make use of CRT for image-displaying purposes.
Cathode Ray Oscilloscope Circuitry
- Vertical Amplifier
- Horizontal amplifier
- Time base Circuit
- Power Supplies
- Cathode Ray Tube
Construction of a CRT –
- The primary components are the heated metal cathode and a control grid.
- The heat is supplied to the cathode (by passing a current through the filament). This way the electrons get heated up and ejected out of the cathode filament.
- This stream of negatively charged electrons is accelerated towards the phosphor screen by supplying a high positive voltage.
- This acceleration is generally produced by means of an accelerating anode.
- The next component is the Focusing System, which is used to force the electron beam to converge to a small spot on the screen.
- If there will not be any focusing system, the electrons will be scattered because of their own repulsions and hence we won’t get a sharp image of the object.
- This focus can be either by means of electrostatic fields or magnetic fields.
Types Of Deflection:
- Electrostatic Deflection: The electron beam (cathode rays) passes through a highly positively charged metal cylinder that forms an electrostatic lens. This electrostatic lens focuses the cathode rays to the center of the screen in the same way as an optical lens focuses the beam of light. Two pairs of parallel plates are mounted inside the CRT tube. The electrostatic deflection sensitivity of a Cathode Ray Tube is the amount of deflection produced in the electron beam when a voltage of 1V is applied between the plates.
- Magnetic Deflection: Here, two pairs of coils are used. One pair is mounted on the top and bottom of the CRT tube, and the other pair is on the two opposite sides. The magnetic field produced by both these pairs is such that a force is generated on the electron beam in a direction perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field and the direction of flow of the beam. One pair is mounted horizontally and the other vertically.